calculator:inductance_of_straight_rectangular_wire
Calculator of inductance of a straight rectangular non-magnetic wire
| | Stan Zurek, Calculator of inductance of a straight rectangular non-magnetic wire, Encyclopedia Magnetica, https://www.e-magnetica.pl/doku.php/calculator/inductance_of_straight_rectangular_wire, {accessed: 2025-03-13} |
| |
|
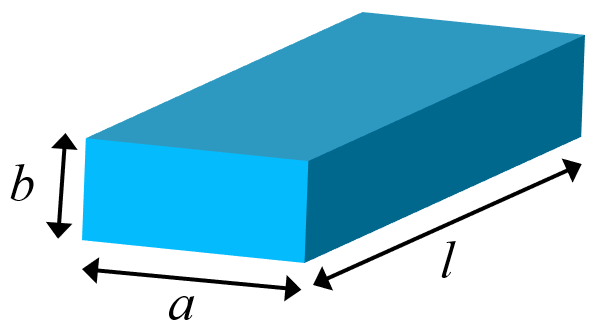
Inductance of a straight wire or conductor with a rectangular or square cross-section can be calculated withe the equations as specified below.
Note: Several assumptions are made for all these equations: 1) The return path is not considered so the total inductance of the complete circuit can be significantly different. 2) The length of the wire is assumed to be significantly longer than its sides (a,b « l), otherwise the calculation errors might be excessive. 3) The medium and the wire are assumed to be non-magnetic with μr ≡ 1. 3) The current is uniformly distributed inside the wire (no skin effect). 4) The equations were converted here to be consistent with SI units.
| Inductance of a straight rectangular non-magnetic wire or conductor | ||
|---|---|---|
| [1] Source: Edward B. Rosa, The self and mutual inductance of linear conductors, Department of Commerce and Labor, Bulletin of the Bureau of Standards, Volume 4, 1907-8, Washington, 1908 | ||
| (1a) Rosa [1], full eq. (21), p. 315 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{2⋅l}{a+b} \right) + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{0.2235⋅(a+b)}{l} \right) $$ | (H) |
| (1b) Rosa [1], simplified eq. (21), p. 315 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{2⋅l}{a+b} \right) + \frac{1}{2} \right) $$ | (H) |
| [2] Source: F.W. Grover, Inductance Calculations: Working Formulas and Tables, ISA, New York, 1982, ISBN 0876645570 | ||
| (2a) Grover [2], full eq. (9), p. 35 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{2⋅l}{a+b} \right) + \frac{1}{2} - G(a,b) \right) $$ | (H) |
| (2b) Grover [2], simplified eq. (9), p. 35 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{2⋅l}{a+b} \right) + \frac{1}{2} - G_{half} \right) $$ | (H) |
| where: $μ_0$ - permeability of vacuum (H/m), $l$ - wire length (m), $a$ and $b$ - side lengths (m) of the rectangular cross-section, $G(a,b)$ - Grover function of Table 3 [2] (unitless) approximated here with 6th degree polynomial as listed below, $G_{half} = 0.00125 $ - a constant set to half of the peak value of the Grover function of Table 3 (unitless), the Grover function depends on the ratio $r = a/b$ or $r = b/a$ (whichever ratio gives the result between 0 and 1), and is approximated here with the following 6th degree polynomial with the intercept forced to 0, just for ease of implementation (rather than using the full Grover's look-up table): | ||
| $G(a,b) = -0.15627 ⋅ r^6 +0.54511 ⋅ r^5-0.75699 ⋅ r^4+0.53460 ⋅ r^3-0.20147 ⋅ r^2+0.03677 ⋅ r + 0 $ | (unitless) | |
↑
| → → → Helpful page? Support us! → → → | PayPal | ← ← ← Help us with just $0.10 per month? Come on…  ← ← ← |
calculator/inductance_of_straight_rectangular_wire.txt · Last modified: 2025/02/09 19:55 by stan_zurek