Calculator of inductance of straight round strands distributed on a circle
| | Stan Zurek, Calculator of inductance of straight round strands distributed on a circle, Encyclopedia Magnetica, https://www.e-magnetica.pl/doku.php/calculator/inductance_of_straight_round_strands_on_circle, {accessed: 2025-03-13} |
| |
|
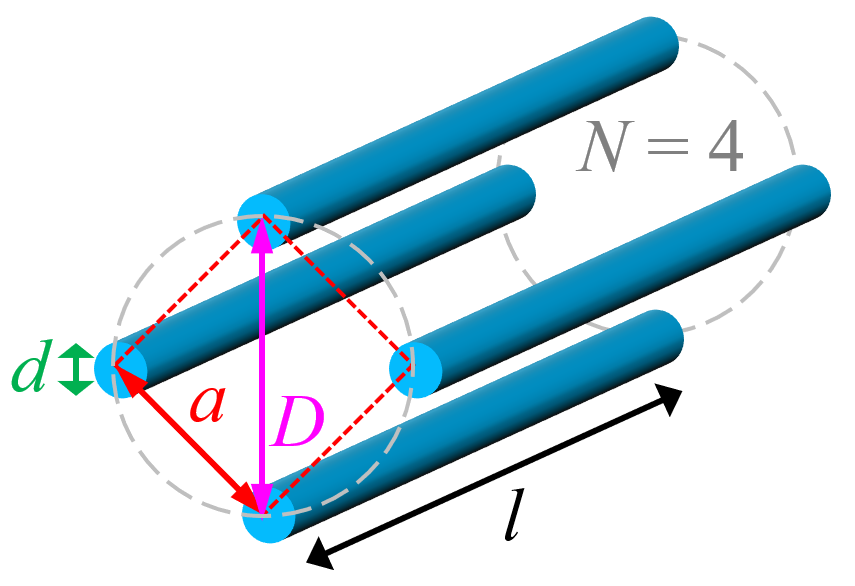
S. Zurek, E-Magnetica.pl, CC-BY-4.0
Inductance of a number N of identical parallel strands, straight wires or conductors, connected in parallel and distributed uniformly on a perimeter of a circle (without current return path) can be calculated with the equations as below.
Equations
Note: Several assumptions are made for all these equations: 1) The return path is not considered so the total inductance of the complete circuit can be significantly different. 2) The length of the wire is assumed to be significantly longer than other dimensions (a,d,D « l), otherwise the calculation errors might be excessive. 3) The medium and the wire are assumed to be non-magnetic with μr = 1. 3) The current is uniformly distributed inside the wire (no skin effect). 4) The equations were re-arranged and converted here to be consistent with SI units, and making use of diameter rather than radius. 5) The circle diameter D is such such that it coincides with the centres of the wires. 6) The calculations may fail for large N (e.g. N > 150), due to limitations of raising to such a large power value.
| Inductance of a several round wires or conductors distributed uniformly on a circle | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [1] Source: F.W. Grover, Inductance Calculations: Working Formulas and Tables, ISA, New York, 1982, ISBN 0876645570 | |||
| for N wires (uniformly spaced, regular polygon) | (1) [1], full eq. (14), p. 37 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π} ⋅ \left( ln \left( \frac{4 ⋅ l}{\sqrt[N]{N ⋅ d ⋅ D^{N-1} }} \right) - \frac{4⋅N-1}{4⋅N} \right) $$ | (H) |
| for N = 3 wires (equilateral triangle) | (2) [1], full eq. (13), p. 37 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{4⋅l}{\sqrt[3]{3⋅d ⋅ D^2}} \right) - \frac{11}{12} \right) $$ | (H) |
| for 2 wires (one on each side of the circle) | (3) [1], full eq. (12), p. 37 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{4⋅l}{\sqrt{2 ⋅ d ⋅ D}} \right) - \frac{7}{8} \right) $$ | (H) |
| for N = 1 wire (single wire, for comparison only) | (4) [1], full eq. (7), p. 35 | $$ L = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π} ⋅ \left( ln \left( \frac{4 ⋅ l}{d} \right) - \frac{3}{4} \right) $$ | (H) |
| where: $μ_0$ - permeability of vacuum (H/m), $l$ - wire length (m), $d$ - diameter (m) of the wire, $D$ - diameter (m) of the circle. | |||
| These equations are based on [1] but were rearranged by S. Zurek to make use of diameter rather than radius, and for SI units. For N = 3 the the length of the side of the triangle (as used in [1]) was calculated as $a = D ⋅ sin(π/3) = \sqrt{3} ⋅ D /2 $ and used for simplifying and unifying the equation, so that only the D input variable is needed. The conversion process is listed here. | |||
| → → → Helpful page? Support us! → → → | PayPal | ← ← ← Help us with just $0.10 per month? Come on…  ← ← ← |
