calculator:inductance_of_straight_tube
Calculator of inductance of a straight tubular conductor
| | Stan Zurek, Calculator of inductance of a straight tubular conductor, Encyclopedia Magnetica, https://www.e-magnetica.pl/doku.php/calculator/inductance_of_straight_tube, {accessed: 2025-03-13} |
| |
|
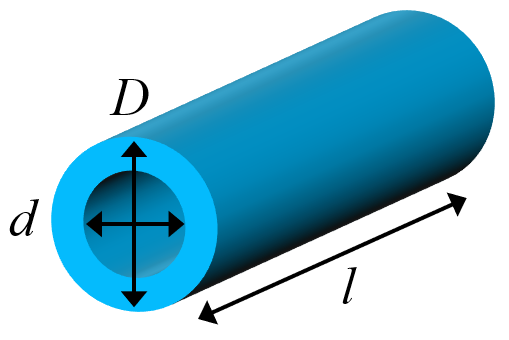
Inductance of a straight round tubular conductor (extruded cylindrical tube or pipe) made from non-magnetic material (relative permeability μr = 1) can be calculated with the the equation as specified below.
Note: Several assumptions are made for all these equations: 1) The return path is not considered so the total inductance of the complete circuit can be significantly different. 2) The length of the wire is assumed to be significantly longer than its diameter(s) (d,D « l), otherwise the calculation errors might be excessive. 3) The conductor and the surrounding medium are assumed to be non-magnetic (μr = 1). 4) The equations were converted here to be consistent with SI units.
| Inductance of a straight round tubular conductor | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sources: [1] F.W. Grover, Inductance Calculations: Working Formulas and Tables, ISA, New York, 1982, ISBN 0876645570 | ||
| (1) [1] Grover, eq. (11), p. 36 | $$ L_{DC} = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{4⋅l}{D} \right) - 1 + ξ_Z \right) $$ | (H) |
| (2) [1] Grover, Chapter 24, p. 261 (AC high-frequency limit) | $$ L_{AC, HF} = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{4⋅l}{D} \right) - 1 \right) $$ | (H) |
| (3) [1] Grover, Chapter 24, p. 261 (DC limit for solid wire) | $$ L_{DC, wire} = \frac{μ_0 ⋅ l}{2⋅π}⋅\left( ln \left( \frac{4⋅l}{D} \right) - \frac{3}{4} \right) $$ | (H) |
| where: $μ_0$ - magnetic permeability of vacuum (H/m), $l$ - wire length (m), $D$ - outer diameter (m) of the tube, $d$ - inner diameter (m) of the tube, $ξ_Z$ - Grover's zeta function (unitless), which is tabulated in [1] Table 4, and can be approximated with the following polynomial (see more): | ||
| (1.1) Grover's Table 4 with Zurek's approximation by polynomials | $$ ξ_Z = 0.1705⋅z^3 - 0.3979⋅z^2 - 0.0214⋅z + 0.25 $$ | (unitless) |
| (1.2) ratio $z$ of diameters | $$ z = d/D $$ | (unitless) |
↑
| → → → Helpful page? Support us! → → → | PayPal | ← ← ← Help us with just $0.10 per month? Come on…  ← ← ← |
calculator/inductance_of_straight_tube.txt · Last modified: 2025/02/08 16:18 by stan_zurek