−Table of Contents
Step Voltage insulation test
| Stan Zurek, Step Voltage insulation test, Encyclopedia Magnetica, https://e-magnetica.pl/doku.php/step_voltage_insulation_test |
Step Voltage insulation test or SV test - a type of insulation resistance test used for diagnosing the quality of electrical insulation, by applying high DC voltage in steps of increasing amplitude.1)2)3)

S. Zurek, E-Magnetica.pl, CC-BY-4.0
The Step Voltage test offers improved diagnostics over a simple DC insulation test. At the end of each step the current reading is taken (spot reading at a given time), and a series of such readings forms a curve, which for a healthy insulation should follow a straight line.
(The test can be also performed by taking spot reading of insulation resistance, but it is widely adopted and recommended by test standards such as IEEE 95 4) to use the current readings.)
If this line of current readings is deformed, especially if it begins to “accelerate” towards higher values for higher voltage then there is a suspicion that the insulation is weakened, so that disproportionately increased amount of current is flowing. The test can be then stopped before a flash-over or breakdown happens, which can permanently damage the insulation.
| → → → Helpful page? Support us! → → → | PayPal | ← ← ← Help us with just $0.10 per month? Come on…  ← ← ← |
S. Zurek, E-Magnetica.pl, CC-BY-4.0
Example of Step Voltage test
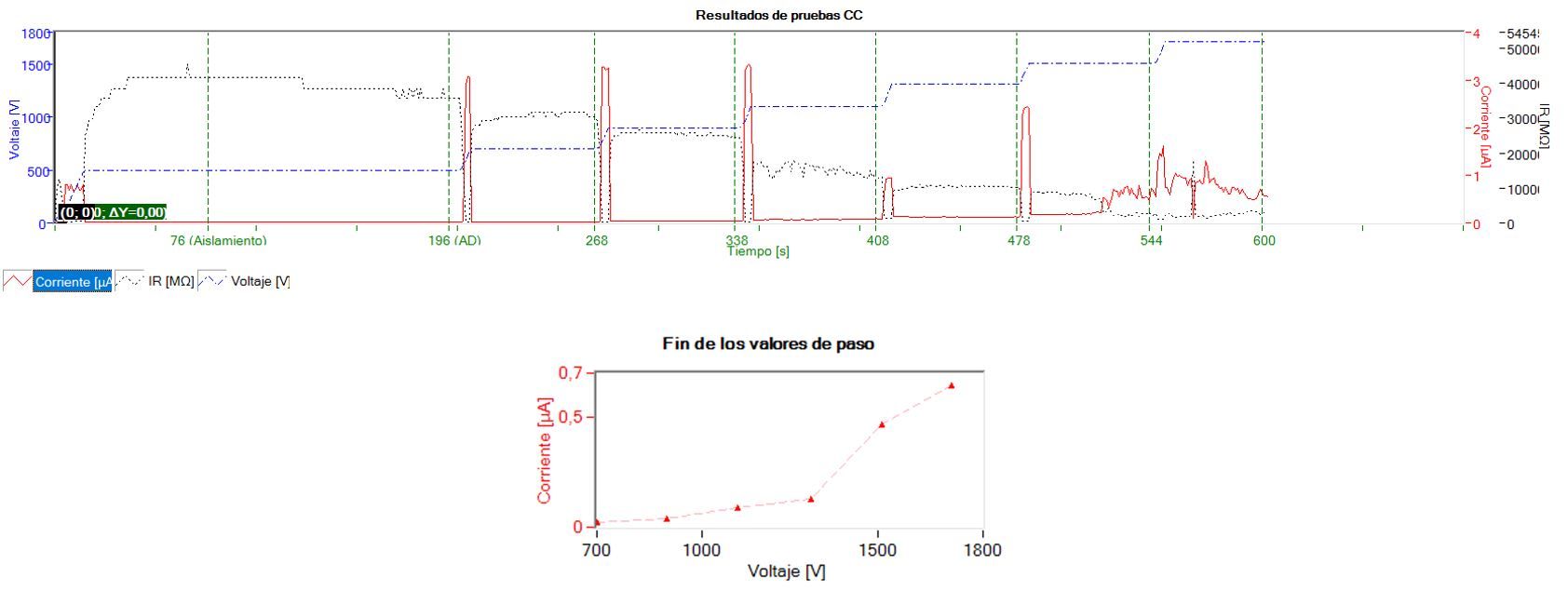
An induction motor 110 kW attached to a pump was undergoing a routine maintenance, and the SV test was applied as per IEEE 95 recommendations.5) The test equipment was Megger Baker DX.
The SV test was set as starting from 7000 V, with 200 V steps, each lasting 60 s, with around 10 s ramping time between the steps.
For the initial 4 steps the current increases roughly linearly with the increased voltage, as expected. However, after reaching 1500 V the current increases rapidly, and the even more so for the next step of 1700 V. In the current waveform it can be seen that in the last step the current readings become, further indicating suspicious behaviour of the insulation.
The diagnosis was that the insulation is compromised and that the motor is to be taken out for servicing. After disassembly, it was visually confirmed that there was a physical damage of insulation, at the exit of one of the core slots (as shown in the picture).
 by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0
by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0
 by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0
by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0
 by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0
by G. Gómez, CC-BY-4.0

